Python Design Patterns - State
它为状态机提供了一个模块,该模块使用从指定的状态机类派生的子类实现。 这些方法与状态无关,并导致使用装饰器声明的转换。
如何实现状态模式?
状态模式的基本实现如下所示 -
class ComputerState(object):
name = "state"
allowed = []
def switch(self, state):
""" Switch to new state """
if state.name in self.allowed:
print 'Current:',self,' => switched to new state',state.name
self.__class__ = state
else:
print 'Current:',self,' => switching to',state.name,'not possible.'
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Off(ComputerState):
name = "off"
allowed = ['on']
class On(ComputerState):
""" State of being powered on and working """
name = "on"
allowed = ['off','suspend','hibernate']
class Suspend(ComputerState):
""" State of being in suspended mode after switched on """
name = "suspend"
allowed = ['on']
class Hibernate(ComputerState):
""" State of being in hibernation after powered on """
name = "hibernate"
allowed = ['on']
class Computer(object):
""" A class representing a computer """
def __init__(self, model='HP'):
self.model = model
# State of the computer - default is off.
self.state = Off()
def change(self, state):
""" Change state """
self.state.switch(state)
if __name__ == "__main__":
comp = Computer()
comp.change(On)
comp.change(Off)
comp.change(On)
comp.change(Suspend)
comp.change(Hibernate)
comp.change(On)
comp.change(Off)
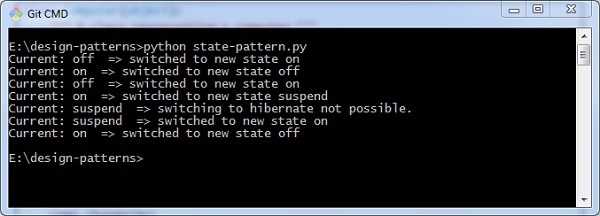
输出 (Output)
上述程序生成以下输出 -